27 UN Data
UNdata: https://data.un.org
Data of World Development Indicators are in a uniform format and downloadable using an R package WDI. So it is easy to handle. However, other data require data transformation to make it tidy. We give a couple of examples. Most of the UN data, they are in CSV, and you can get a link quickly, or download it by clicking. Though the data structure is not uniform, it is relatively easy to handle.
27.1 Setup
library(tidyverse)
#> ── Attaching core tidyverse packages ──── tidyverse 2.0.0 ──
#> ✔ dplyr 1.1.3 ✔ readr 2.1.4
#> ✔ forcats 1.0.0 ✔ stringr 1.5.0
#> ✔ ggplot2 3.4.4 ✔ tibble 3.2.1
#> ✔ lubridate 1.9.3 ✔ tidyr 1.3.0
#> ✔ purrr 1.0.2
#> ── Conflicts ────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
#> ✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
#> ✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
#> ℹ Use the conflicted package (<http://conflicted.r-lib.org/>) to force all conflicts to become errors
wdi_cache <- read_rds("./data/wdi_cache.RData")27.2 Importing UN Data
Since most of the UN data are available in CSV format, if you obtain the link, i.e., url, to the file, you can use read_csv(url) to load the data. Alternatively, you can download the file to your download folder. Then move the file to the data directory of your project. You can load it by read_csv("./data/file_name").
27.3 Examples
27.3.1 Education
By the following, you can see that the first row is not the column name. R gives column names such as …1, …2, etc., when the column name is void.
You can copy the link (url) by right click or ctrl+click.
url_un_edu <- "https://data.un.org/_Docs/SYB/CSV/SYB65_309_202209_Education.csv"Let is skip the first row by adding skip = 1.
#> Rows: 7282 Columns: 7
#> ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────
#> Delimiter: ","
#> chr (4): ...2, Series, Footnotes, Source
#> dbl (3): Region/Country/Area, Year, Value
#>
#> ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
#> ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
#> # A tibble: 10 × 7
#> `Region/Country/Area` ...2 Year Series Value Footnotes
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 1 Tota… 2005 Stude… 6.79e5 <NA>
#> 2 1 Tota… 2005 Gross… 1.05e2 <NA>
#> 3 1 Tota… 2005 Gross… 9.97e1 <NA>
#> 4 1 Tota… 2005 Stude… 5.09e5 <NA>
#> 5 1 Tota… 2005 Gross… 6.58e1 <NA>
#> 6 1 Tota… 2005 Gross… 6.23e1 <NA>
#> 7 1 Tota… 2005 Stude… 2.00e5 <NA>
#> 8 1 Tota… 2005 Gross… 5.12e1 <NA>
#> 9 1 Tota… 2005 Gross… 4.83e1 <NA>
#> 10 1 Tota… 2010 Stude… 6.97e5 <NA>
#> # ℹ 1 more variable: Source <chr>It is a very large data, and we need to check the values.
summary(un_edu)
#> Region/Country/Area ...2 Year
#> Min. : 1.0 Length:7282 Min. :2000
#> 1st Qu.:178.0 Class :character 1st Qu.:2005
#> Median :417.0 Mode :character Median :2010
#> Mean :408.8 Mean :2012
#> 3rd Qu.:626.0 3rd Qu.:2015
#> Max. :894.0 Max. :2021
#> Series Value Footnotes
#> Length:7282 Min. : 0.0 Length:7282
#> Class :character 1st Qu.: 71.6 Class :character
#> Mode :character Median : 100.2 Mode :character
#> Mean : 2534.7
#> 3rd Qu.: 133.6
#> Max. :750125.0
#> Source
#> Length:7282
#> Class :character
#> Mode :character
#>
#>
#> We can see that the Year is from 2000 to 2021. The first variable, Region/Country/Area and the fifth variable, Value are dbl, i.e., double; hence, these are numerical variables, and you can see them from the summary as well. But it is not easy to see other variables. Let us try them one by one.
un_edu %>% distinct(...2)
#> # A tibble: 224 × 1
#> ...2
#> <chr>
#> 1 Total, all countries or areas
#> 2 Northern Africa
#> 3 Sub-Saharan Africa
#> 4 Northern America
#> 5 Latin America & the Caribbean
#> 6 Central Asia
#> 7 Eastern Asia
#> 8 South-eastern Asia
#> 9 Southern Asia
#> 10 Western Asia
#> # ℹ 214 more rows
un_edu %>% distinct(Series)
#> # A tibble: 9 × 1
#> Series
#> <chr>
#> 1 Students enrolled in primary education (thousands)
#> 2 Gross enrollment ratio - Primary (male)
#> 3 Gross enrollment ratio - Primary (female)
#> 4 Students enrolled in secondary education (thousands)
#> 5 Gross enrollment ratio - Secondary (male)
#> 6 Gross enrollment ratio - Secondary (female)
#> 7 Students enrolled in upper secondary education (thousands)
#> 8 Gross enrollment ratio - Upper secondary level (male)
#> 9 Gross enrollment ratio - Upper secondary level (female)
un_edu %>% distinct(Source)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 1
#> Source
#> <chr>
#> 1 United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organ…- We may need to handle Footnotes carefully later, but for the first exploration, we need, …2 for Region, Year, Series, Values.
df_un_edu <- un_edu %>%
select(Region = ...2, Year, Series, Value)
df_un_edu
#> # A tibble: 7,282 × 4
#> Region Year Series Value
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 Total, all countries or areas 2005 Students enro… 6.79e5
#> 2 Total, all countries or areas 2005 Gross enrollm… 1.05e2
#> 3 Total, all countries or areas 2005 Gross enrollm… 9.97e1
#> 4 Total, all countries or areas 2005 Students enro… 5.09e5
#> 5 Total, all countries or areas 2005 Gross enrollm… 6.58e1
#> 6 Total, all countries or areas 2005 Gross enrollm… 6.23e1
#> 7 Total, all countries or areas 2005 Students enro… 2.00e5
#> 8 Total, all countries or areas 2005 Gross enrollm… 5.12e1
#> 9 Total, all countries or areas 2005 Gross enrollm… 4.83e1
#> 10 Total, all countries or areas 2010 Students enro… 6.97e5
#> # ℹ 7,272 more rowsIs there a way to separate regions from countries?
df_un_edu %>% left_join(wdi_cache$country, by = c("Region"="country")) %>%
filter(!is.na(iso2c)) %>% distinct(Region)
#> # A tibble: 176 × 1
#> Region
#> <chr>
#> 1 Afghanistan
#> 2 Albania
#> 3 Algeria
#> 4 Andorra
#> 5 Angola
#> 6 Antigua and Barbuda
#> 7 Argentina
#> 8 Armenia
#> 9 Aruba
#> 10 Australia
#> # ℹ 166 more rows
df_un_edu %>% left_join(wdi_cache$country, by = c("Region"="country")) %>%
filter(is.na(iso2c)) %>% distinct(Region)
#> # A tibble: 48 × 1
#> Region
#> <chr>
#> 1 Total, all countries or areas
#> 2 Northern Africa
#> 3 Sub-Saharan Africa
#> 4 Northern America
#> 5 Latin America & the Caribbean
#> 6 Central Asia
#> 7 Eastern Asia
#> 8 South-eastern Asia
#> 9 Southern Asia
#> 10 Western Asia
#> # ℹ 38 more rows
df_un_edu %>% left_join(wdi_cache$country, by = c("Region"="country")) %>%
filter(is.na(iso2c)) %>% distinct(Region) %>% pull()
#> [1] "Total, all countries or areas"
#> [2] "Northern Africa"
#> [3] "Sub-Saharan Africa"
#> [4] "Northern America"
#> [5] "Latin America & the Caribbean"
#> [6] "Central Asia"
#> [7] "Eastern Asia"
#> [8] "South-eastern Asia"
#> [9] "Southern Asia"
#> [10] "Western Asia"
#> [11] "Europe"
#> [12] "Oceania"
#> [13] "Anguilla"
#> [14] "Bahamas"
#> [15] "Bolivia (Plurin. State of)"
#> [16] "China, Hong Kong SAR"
#> [17] "China, Macao SAR"
#> [18] "Congo"
#> [19] "Cook Islands"
#> [20] "Côte d’Ivoire"
#> [21] "Curaçao"
#> [22] "Dem. People's Rep. Korea"
#> [23] "Dem. Rep. of the Congo"
#> [24] "Egypt"
#> [25] "Gambia"
#> [26] "Holy See"
#> [27] "Iran (Islamic Republic of)"
#> [28] "Kyrgyzstan"
#> [29] "Lao People's Dem. Rep."
#> [30] "Micronesia (Fed. States of)"
#> [31] "Montserrat"
#> [32] "Netherlands Antilles [former]"
#> [33] "Niue"
#> [34] "Republic of Korea"
#> [35] "Republic of Moldova"
#> [36] "Saint Kitts and Nevis"
#> [37] "Saint Lucia"
#> [38] "Saint Vincent & Grenadines"
#> [39] "Slovakia"
#> [40] "State of Palestine"
#> [41] "Sudan [former]"
#> [42] "Tokelau"
#> [43] "Türkiye"
#> [44] "United Rep. of Tanzania"
#> [45] "United States of America"
#> [46] "Venezuela (Boliv. Rep. of)"
#> [47] "Viet Nam"
#> [48] "Yemen"There are some countries iso2c is not properly assigned. From the list above, Probably, the first 12 are areas and the value contains the aggregated value.
area <- df_un_edu %>% distinct(Region) %>% slice(1:12) %>% pull()
area
#> [1] "Total, all countries or areas"
#> [2] "Northern Africa"
#> [3] "Sub-Saharan Africa"
#> [4] "Northern America"
#> [5] "Latin America & the Caribbean"
#> [6] "Central Asia"
#> [7] "Eastern Asia"
#> [8] "South-eastern Asia"
#> [9] "Southern Asia"
#> [10] "Western Asia"
#> [11] "Europe"
#> [12] "Oceania"
un_edu_area <- df_un_edu %>% filter(Region %in% area)
un_edu_region <- df_un_edu %>% filter(!Region %in% area)Now we can start studying the data.
un_edu_area %>%
filter(Series %in% c("Gross enrollment ratio - Upper secondary level (male)", "Gross enrollment ratio - Upper secondary level (female)")) %>%
ggplot(aes(Year, Value, color = Region, linetype = Series)) + geom_line()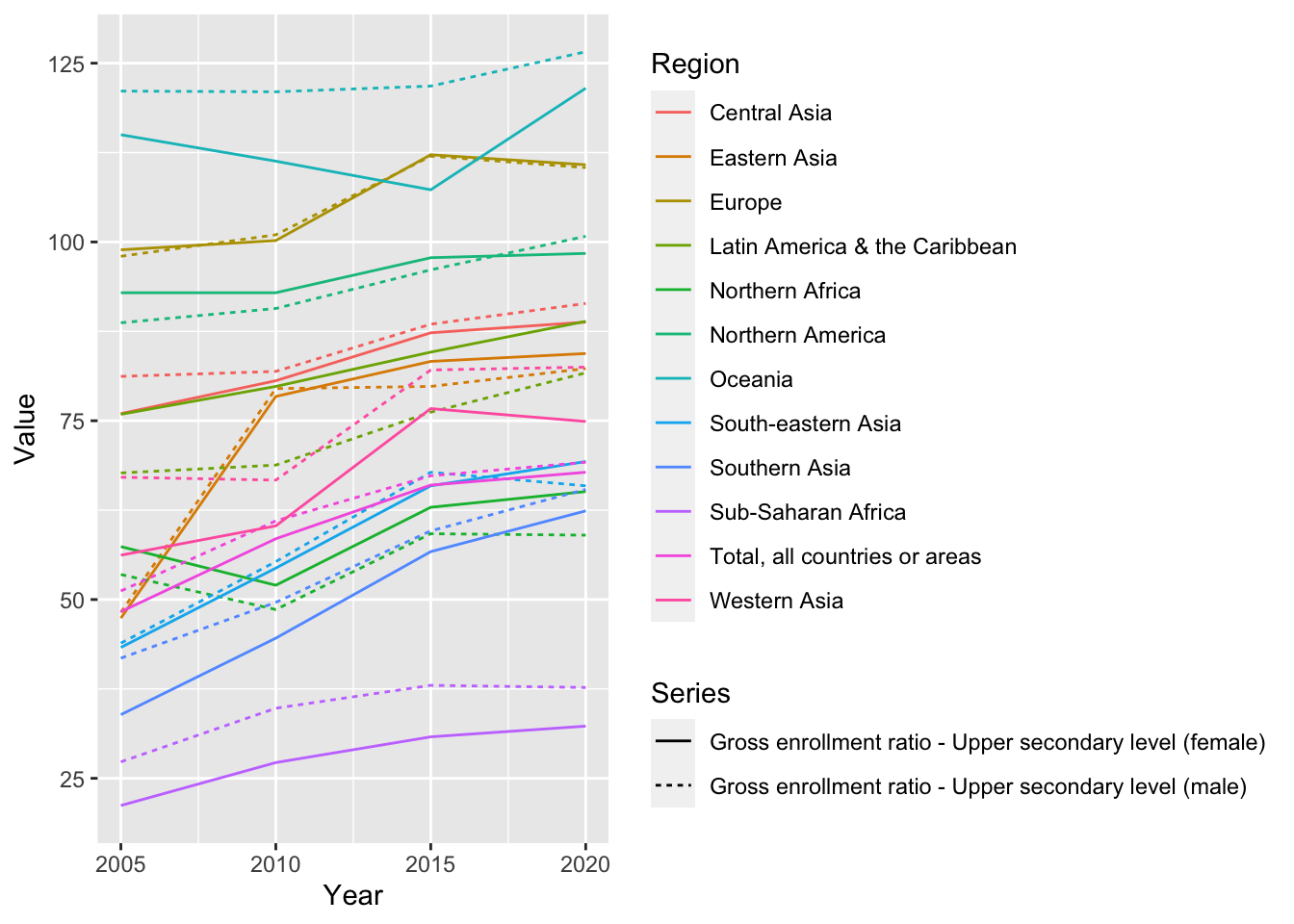
un_edu_area %>%
filter(Series %in% c("Gross enrollment ratio - Upper secondary level (male)", "Gross enrollment ratio - Upper secondary level (female)")) %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = Series, values_from = Value) %>%
mutate (Ratio = `Gross enrollment ratio - Upper secondary level (female)`/`Gross enrollment ratio - Upper secondary level (male)`) %>%
ggplot(aes(Year, Ratio, color = Region, linetype = Region)) + geom_line() +
labs(title = "Upper Secondary Level Education", subtitle = "Ratio = female/male")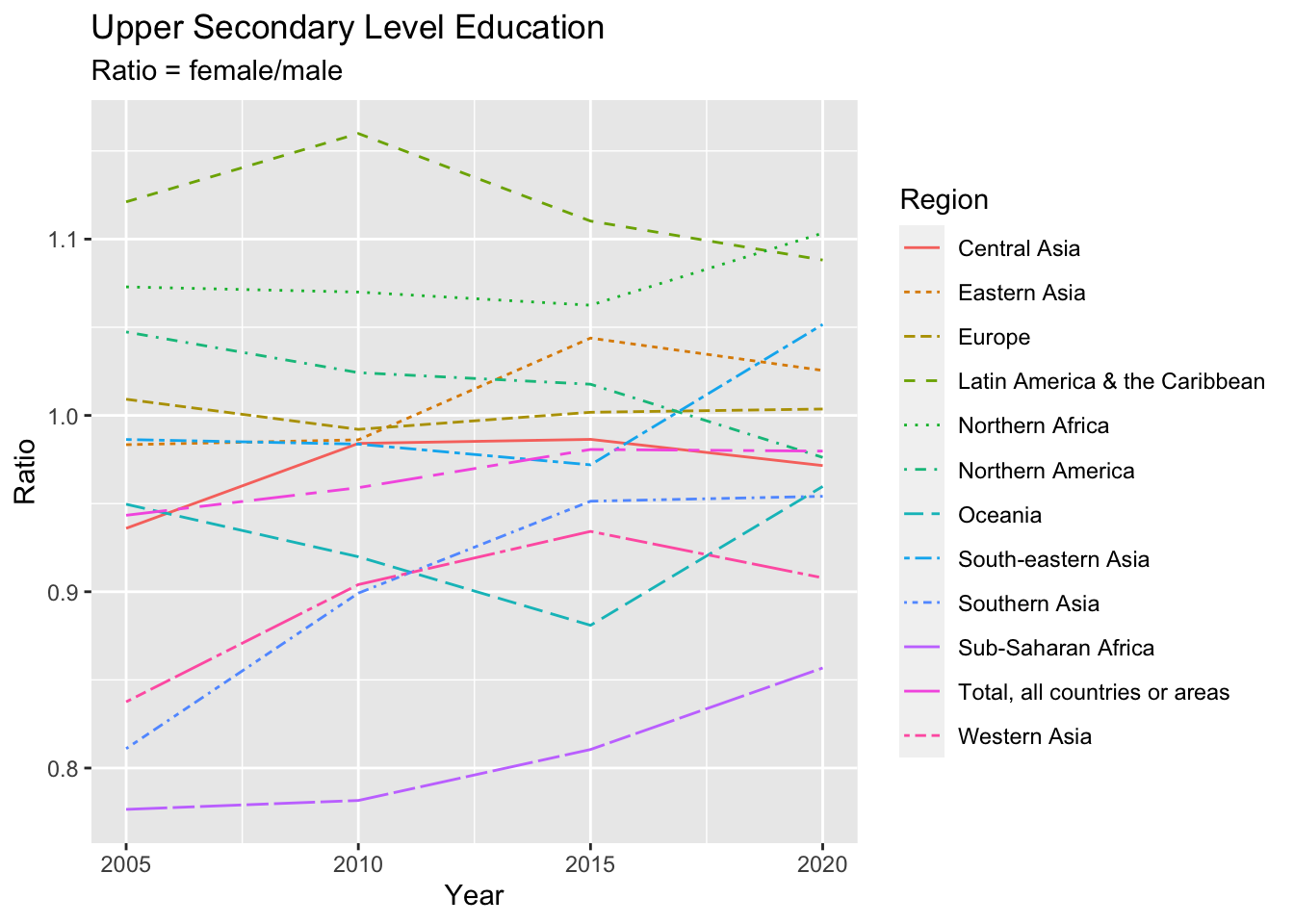
27.3.2 Population
Data structure is similar to the previous one. So use skip=1, and check the variable s briefly.
url_un_pop = "https://data.un.org/_Docs/SYB/CSV/SYB65_246_202209_Population%20Growth,%20Fertility%20and%20Mortality%20Indicators.csv"
df_un_pop <- read.csv(url_un_pop, skip = 1)
df_un_pop#> Rows: 6654 Columns: 7
#> ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────
#> Delimiter: ","
#> chr (4): X, Series, Footnotes, Source
#> dbl (2): Region.Country.Area, Year
#> num (1): Value
#>
#> ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
#> ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
#> # A tibble: 10 × 7
#> Region.Country.Area X Year Series Value Footnotes
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 1 Total, … 2010 Popul… 1.3 <NA>
#> 2 1 Total, … 2010 Total… 2.6 <NA>
#> 3 1 Total, … 2010 Infan… 37.1 <NA>
#> 4 1 Total, … 2010 Mater… 253 <NA>
#> 5 1 Total, … 2010 Life … 70.1 <NA>
#> 6 1 Total, … 2010 Life … 67.6 <NA>
#> 7 1 Total, … 2010 Life … 72.7 <NA>
#> 8 1 Total, … 2015 Popul… 1.2 <NA>
#> 9 1 Total, … 2015 Total… 2.5 <NA>
#> 10 1 Total, … 2015 Infan… 31.5 <NA>
#> # ℹ 1 more variable: Source <chr>
df_un_pop %>% distinct(Source)
#> # A tibble: 4 × 1
#> Source
#> <chr>
#> 1 "United Nations Population Division, New York, World Popu…
#> 2 "United Nations Population Division, New York, World Popu…
#> 3 "United Nations Statistics Division, New York, \"Demograp…
#> 4 "World Health Organization (WHO), the United Nations Chil…
df_un_pop %>% distinct(Footnotes)
#> # A tibble: 82 × 1
#> Footnotes
#> <chr>
#> 1 <NA>
#> 2 Projected estimate (medium fertility variant).
#> 3 Including Saint Helena.
#> 4 Projected estimate (medium fertility variant).;Including…
#> 5 Including Bermuda, Greenland, and Saint Pierre and Mique…
#> 6 Projected estimate (medium fertility variant).;Including…
#> 7 Including Anguilla, Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba, Br…
#> 8 Projected estimate (medium fertility variant).;Including…
#> 9 Including Falkland Islands (Malvinas).
#> 10 Projected estimate (medium fertility variant).;Including…
#> # ℹ 72 more rows
df_un_pop %>% distinct(X)
#> # A tibble: 264 × 1
#> X
#> <chr>
#> 1 Total, all countries or areas
#> 2 Africa
#> 3 Northern Africa
#> 4 Sub-Saharan Africa
#> 5 Eastern Africa
#> 6 Middle Africa
#> 7 Southern Africa
#> 8 Western Africa
#> 9 Northern America
#> 10 Latin America & the Caribbean
#> # ℹ 254 more rows
df_un_pop %>% distinct(Series)
#> # A tibble: 7 × 1
#> Series
#> <chr>
#> 1 Population annual rate of increase (percent)
#> 2 Total fertility rate (children per women)
#> 3 Infant mortality for both sexes (per 1,000 live births)
#> 4 Maternal mortality ratio (deaths per 100,000 population)
#> 5 Life expectancy at birth for both sexes (years)
#> 6 Life expectancy at birth for males (years)
#> 7 Life expectancy at birth for females (years)- Footnotes need to be studied.
- There are four different sources.
- X is for the region, the first 30 are areas, and the rest are countries or regions.
- There are seven series. It may be easier if we assign shorter names for each value.
pop_area <- df_un_pop %>% distinct(X) %>% slice(1:30) %>% pull()
pop_area
#> [1] "Total, all countries or areas"
#> [2] "Africa"
#> [3] "Northern Africa"
#> [4] "Sub-Saharan Africa"
#> [5] "Eastern Africa"
#> [6] "Middle Africa"
#> [7] "Southern Africa"
#> [8] "Western Africa"
#> [9] "Northern America"
#> [10] "Latin America & the Caribbean"
#> [11] "Caribbean"
#> [12] "Central America"
#> [13] "South America"
#> [14] "Asia"
#> [15] "Central Asia"
#> [16] "Eastern Asia"
#> [17] "South-central Asia"
#> [18] "South-eastern Asia"
#> [19] "Southern Asia"
#> [20] "Western Asia"
#> [21] "Europe"
#> [22] "Eastern Europe"
#> [23] "Northern Europe"
#> [24] "Southern Europe"
#> [25] "Western Europe"
#> [26] "Oceania"
#> [27] "Australia and New Zealand"
#> [28] "Melanesia"
#> [29] "Micronesia"
#> [30] "Polynesia"
un_pop <- df_un_pop %>% select(Region = X, Year, Series, Value)
un_pop
#> # A tibble: 6,654 × 4
#> Region Year Series Value
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 Total, all countries or areas 2010 Population ann… 1.3
#> 2 Total, all countries or areas 2010 Total fertilit… 2.6
#> 3 Total, all countries or areas 2010 Infant mortali… 37.1
#> 4 Total, all countries or areas 2010 Maternal morta… 253
#> 5 Total, all countries or areas 2010 Life expectanc… 70.1
#> 6 Total, all countries or areas 2010 Life expectanc… 67.6
#> 7 Total, all countries or areas 2010 Life expectanc… 72.7
#> 8 Total, all countries or areas 2015 Population ann… 1.2
#> 9 Total, all countries or areas 2015 Total fertilit… 2.5
#> 10 Total, all countries or areas 2015 Infant mortali… 31.5
#> # ℹ 6,644 more rowsLet us change the names of series.
un_pop_wide <- un_pop %>% pivot_wider(names_from = Series, values_from = Value)
colnames(un_pop_wide) <- c("Region", "Year", "IncRate", "Fert", "InfDeath", "MatDeath", "LifeExp", "LifeExpM", "LifeExpF")
un_pop_wide
#> # A tibble: 1,005 × 9
#> Region Year IncRate Fert InfDeath MatDeath LifeExp
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Total, all… 2010 1.3 2.6 37.1 253 70.1
#> 2 Total, all… 2015 1.2 2.5 31.5 225 71.8
#> 3 Total, all… 2017 1.1 2.5 29.6 218 72.3
#> 4 Total, all… 2022 0.8 2.3 27.5 NA 71.7
#> 5 Africa 2010 2.6 4.9 60.9 NA 58.6
#> 6 Africa 2015 2.6 4.6 52.5 NA 61.1
#> 7 Africa 2022 2.3 4.2 44.2 NA 62.2
#> 8 Northern A… 2010 1.9 3.2 29.5 148 69.6
#> 9 Northern A… 2015 2.1 3.4 25.3 120 70.9
#> 10 Northern A… 2017 2 3.2 24.2 115 71.5
#> # ℹ 995 more rows
#> # ℹ 2 more variables: LifeExpM <dbl>, LifeExpF <dbl>
un_pop_long <- un_pop_wide %>% pivot_longer(cols = -c(1,2), names_to = "Series", values_to = "Value")
un_pop_long
#> # A tibble: 7,035 × 4
#> Region Year Series Value
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 Total, all countries or areas 2010 IncRate 1.3
#> 2 Total, all countries or areas 2010 Fert 2.6
#> 3 Total, all countries or areas 2010 InfDeath 37.1
#> 4 Total, all countries or areas 2010 MatDeath 253
#> 5 Total, all countries or areas 2010 LifeExp 70.1
#> 6 Total, all countries or areas 2010 LifeExpM 67.6
#> 7 Total, all countries or areas 2010 LifeExpF 72.7
#> 8 Total, all countries or areas 2015 IncRate 1.2
#> 9 Total, all countries or areas 2015 Fert 2.5
#> 10 Total, all countries or areas 2015 InfDeath 31.5
#> # ℹ 7,025 more rows
un_pop_long_area <- un_pop_long %>% filter(Region %in% pop_area)
un_pop_long_region <- un_pop_long %>% filter(!Region %in% pop_area)
un_pop_wide_area <- un_pop_wide %>% filter(Region %in% pop_area)
un_pop_wide_region <- un_pop_wide %>% filter(!Region %in% pop_area)Now we can visualize data.